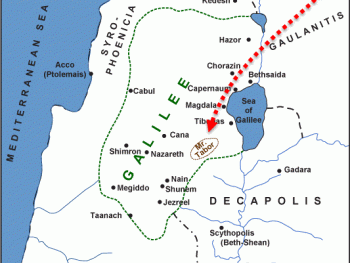
The classes of citizenship (civitus) and legal status in ancient Rome varied over the centuries. When Rome conquered a city the defeated people would fall into one of four classes. Citizens, Municipia, Latin Allies, and Italian Allies.
Other areas maintained their domestic independence but Rome dictated their foreign policies.
Citizenship was extremely important in Rome’s attempt to preserve her unity. When Rome conquered a city they would offer it alliance and would write up various terms of the treaty.
Citizens had full rights and full privileges.
Municipia received Roman citizenship without the right to vote. They were allowed a local self-government and the rights of trade. They also served in the army and paid taxes.
Latin Allies had no citizenship but were allowed the rights of trade, they also equipped Rome with foreign legions and were self-governed.
Italian Allies were Roman protectorates. They sent troop levies to Rome, and they shared in the spoils of war.
Source: